
The Turkish market has revised upward its expectations for year-end inflation and the U.S. dollar exchange rate, while slightly lowering its growth projections, the Central Bank of the Republic of Türkiye (CBRT) reported in its latest monthly survey.
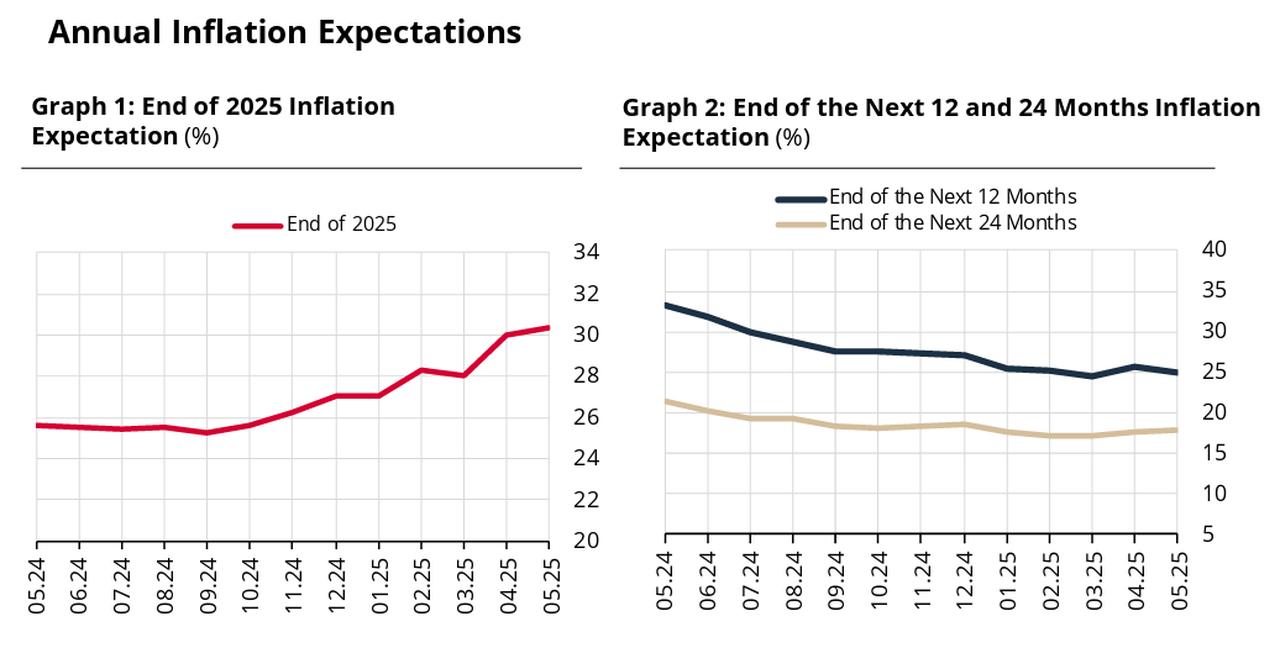
According to the CBRT’s Survey of Market Participants for May, monthly inflation is projected at 2.36%. The average year-end consumer inflation forecast—referred to locally as Türkiye’s Consumer Price Index (TUFE)—rose to 30.35%, up from 29.98% in the previous survey. The 12-month forward inflation expectation eased to 25.06%, down from 25.56%, while the 24-month forecast edged slightly higher to 17.77%, from 17.69%.
Survey respondents now expect the overnight interest rate in the Borsa Istanbul (BIST) Repo and Reverse Repo Market to rise to 49%, compared to 46% in the previous survey round.
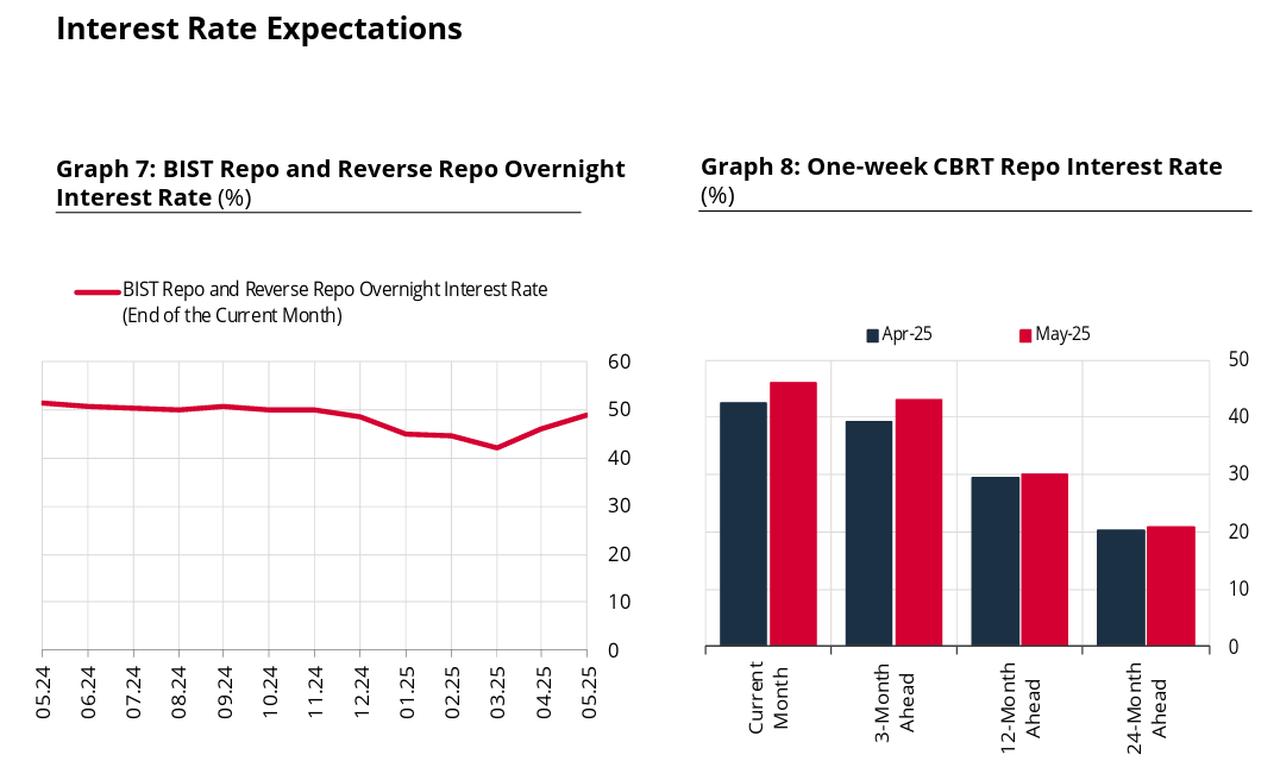
Likewise, the projected interest rate for the CBRT’s one-week repo auctions—commonly regarded as the main policy rate—has been lifted to 42.96%, up from 39.24%, indicating that investors foresee further policy tightening in the coming months.
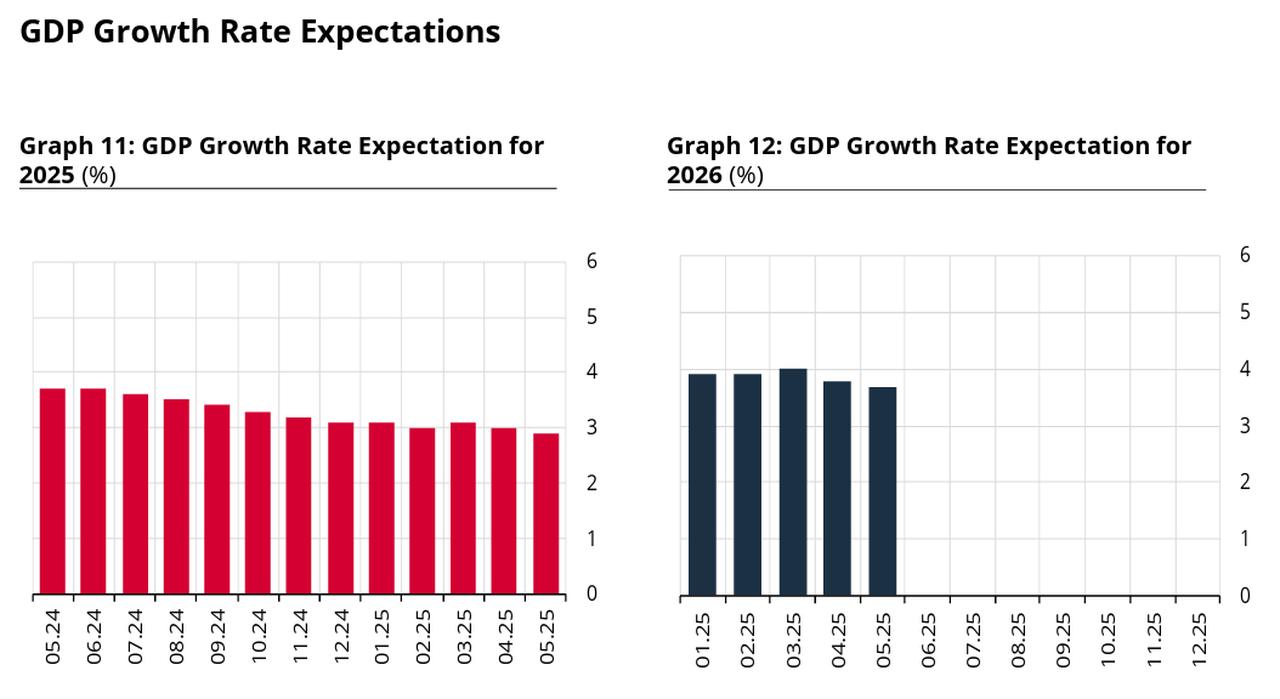
Alongside rising interest rate forecasts, market participants have also revised their expectations for economic growth. The GDP growth projection for 2025 has been trimmed to 2.9% from 3.0%, while the outlook for 2026 has been lowered to 3.7% from the earlier estimate of 3.8%, reflecting concerns about slowing economic momentum under the current disinflationary stance.
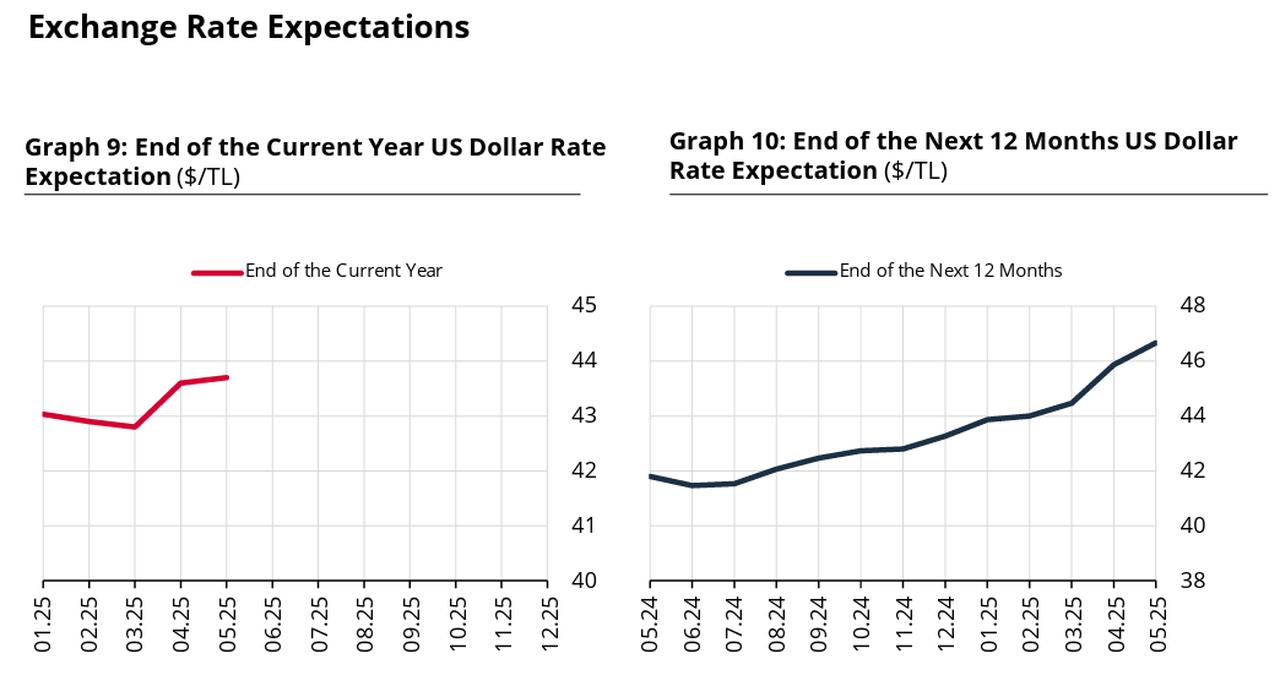
Meanwhile, expectations for the exchange rate have continued to shift upward. The year-end forecast for the U.S. dollar against the Turkish lira has been revised slightly higher to 43.7 from 43.6, while the 12-month projection now stands at 46.62, up from 45.85, suggesting persistent depreciation pressures on the lira.
Türkiye has been sustaining a disinflation program since mid-2023 as part of a broader policy shift to contain soaring prices, after inflation surged to a peak of 75.5% in May 2024—marking the highest level in over two decades. As part of this effort, the CBRT has significantly tightened monetary policy, prompting financial markets to adjust their expectations accordingly.